Tamil Nadu Board 10th Standard Social Science - Geography Unit 4: Book Back Answers and Solutions
This post covers the book back answers and solutions for Unit 4 – Geography from the Tamil Nadu State Board 10th Standard Social Science textbook. These detailed answers have been carefully prepared by our expert teachers at KalviTips.com.
We have explained each answer in a simple, easy-to-understand format, highlighting important points step by step under the relevant subtopics. Students are advised to read and memorize these subtopics thoroughly. Once you understand the main concepts, you’ll be able to connect other related points with real-life examples and confidently present them in your tests and exams.
By going through this material, you’ll gain a strong understanding of Geography Unit 4 along with the corresponding book back questions and answers (PDF format).
Question Types Covered:
- 1 Mark Questions: Choose the correct answer, Fill in the blanks, Identify the correct statement, Match the following
- 2 Mark Questions: Answer briefly
- 3, 4, and 5 Mark Questions: Answer in detail
All answers are presented in a clear and student-friendly manner, focusing on key points to help you score full marks.
All the best, Class 10 students! Prepare well and aim for top scores. Thank you!
Unit 4: India - Resources and Industries
I. Choose the correct answer.
1. Manganese is used in _____.a) Paper industry
b) Steel making
c) Copper smelting
d) Petroleum Refining
Answer Key:
b) Steel making
2. The Anthracite coal has _____.
a) 80 to 90% Carbon
b) Above 70% Carbon
c) 60 to 70% Carbon
d) Below 50% Carbon
Answer Key:
a) 80 to 90% Carbon
3. The most important constituents of petroleum are hydrogen and ____.
a) Oxygen
b) Water
c) Carbon
d) Nitrogen
Answer Key:
c) Carbon
4. The city which is called as the Manchester of South India is _____.
a) Chennai
b) Salem
c) Madurai
d) Coimbatore
Answer Key:
d) Coimbatore
5. The first Nuclear Power station was commissioned in _____.
a) Gujarat
b) Rajasthan
c) Maharashtra
d) Tamil Nadu
Answer Key:
c) Maharashtra
6. The most abundant source of energy is _____.
a) Bio mass
b) Sun
c) Coal
d) Oil
Answer Key:
b) Sun
7. The nucleus for the development of the Chotanagpur plateau region is _____.
a) Transport
b) Mineral Deposits
c) Large demand
d) Power Availability
Answer Key:
b) Mineral Deposits
II. Match the following.
|
1
|
Bauxite
|
Cement
|
|
2
|
Gypsum
|
Aluminium
|
|
3
|
Anthracite
|
Electrical goods
|
|
4
|
Iron ore
|
Coal
|
|
5
|
Mica
|
Magnetite
|
|
1
|
Bauxite
|
Aluminium
|
|
2
|
Gypsum
|
Cement
|
|
3
|
Anthracite
|
Coal
|
|
4
|
Iron ore
|
Magnetite
|
|
5
|
Mica
|
Electrical goods
|
III. Answer the following questions briefly.
1. Define the resource and state its types.Answer Key:
1. Natural resource is any matter or energy derived from the environment and used by living things including humans.
2. It includes water, air, soil, minerals, fossil fuels, plants, wildlife etc. Resources are of two kinds
E.g. : Solar energy and wind energy.
E.g. : Petroleum and coal.
2. What are minerals and state its type?
Answer Key:
1. Minerals are natural substances with specific chemical and physical properties.
2. They are organic and inorganic in nature.
3. There are two types of minerals.
Metallic Minerals - Gold, Copper, Iron and Lead
Non Metallic Minerals - Mica, Limestone, Gypsum, Coal and Petroleum.
3. State the uses of Manganese.
Answer Key:
1. Manganese is the most important mineral for making iron and steel.
2. Nearly 10 kg manganese is required for manufacturing one ton of steel.
3. It is also used in the manufacturing of bleaching powder, insecticides, paints and batteries.
4. What is natural gas?
Answer Key:
1. Natural gas occurs in nature. It is Hydro carbon gas mixture and consists of methane.
2. Petroleum accumulation is the cause.
3. It consists of higher Alkanes. It has also carbon dioxide, Nitrogen and Hydrogen sulphide.
4. It is formed due to the decomposed plants and animals exposed to severe heat and pressure for thousands of years.
5. Name the different types of coal with their carbon content.
Answer Key:
1. Anthracite (80 - 90% carbon)
2. Bituminous (60 - 80% carbon)
3. Lignite (40 - 60% carbon)
4. Peat (less than 40% carbon)
6. Mention the major areas of jute production in India.
Answer Key:
1. West Bengal - along Hooghly river within the radius of 6km of Kolkatta.
2. Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, Chattisgarh and Odisha are the other Jute goods producing areas.
7. Name the important oil producing regions of India.
Answer Key:
|
Western
coast off shore
|
Eastern
Coast off shore
|
|
|
1
|
Mumbai High oil fields
|
Brahmaputra valley
|
|
2
|
Gujarat coast
|
Digboi oil feilds
|
|
3
|
Basseim oil field
|
Nahoratiya oil fields
|
|
4
|
Aliabet oil field
|
Moran-Hugrijan oil field
|
|
5
|
Ankleshwar
|
Rudrasagar-Lawa oil feilds
|
|
6
|
Cambay-Luni Region
|
Surma valley
|
IV. Distinguish between.
1. Renewable and non-renewable resources.Answer Key:
|
Renewable
resources
|
Non-renewable resources
|
|
Naturally replenished after use.
|
Cannot be replenished after use.
|
|
Solar energy, Wind energy, Bio
gas, Tidal energy are renewable.
|
Coal, Petroleum and Natural gas
are not
renewable.
|
|
Pollution free
|
Cause pollution
|
|
TamilNadu Aralvaimozhi -
Windmill
|
Jharkhand, largest coal
producing state
|
Answer Key:
|
Metallic
minerals
|
Non-metallic minerals
|
|
Contain one or more metallic
elements.
|
Do not contain metals in them.
|
|
Iron, Manganese, Copper,
Bauxite, Nickel, Zinc, Lead and Gold are metallic minerals.
|
Mica, Limestone, Gypsum,
Nitrate, Potash, dolomite, Coal are non metallic minerals.
|
Answer Key:
|
Agro - based
industry
|
Mineral - based industry
|
|
Draw raw material from agriculture
sector.
|
They use both metallic and non –
metallic minerals as raw material.
|
|
Cotton Textile, Jute, Silk, and
Sugar industries are agro - based.
|
Iron and Steel is the major
mineral - based
industry.
|
Answer Key:
|
Jute industry
|
Sugar industry
|
|
Jute is the raw material.
|
Sugarcane is the raw material.
|
|
India is the largest producer of
Jute in the world.
|
India is the second largest
producer of sugarcane.
|
|
After cotton textiles, Jute is
the second largest textile industry.
|
It is the second largest agro –
based industry.
|
|
West Bengal is the major
producer of Jute.
|
Uttar Pradesh is the major sugar
producing state.
|
V. Answer the following in a paragraph.
1. Write about the distribution of cotton textile industries in India.Answer Key:
1. Cotton textile industries are Agro - based.
2. Handloom, handicrafts and small power looms provide large employment for
millions of rural people and in semi - urban areas.
3. India is the third largest producer of cotton in the world. It is the largest organised
sector in the country.
4. Mumbai is called the “Manchester of India” as it has the largest concentration of
textile mills.
High concentration in Mumbai ( reasons)
1. Presence of black cotton soil.
2. Availability of hydro power.
3. Humid climate for textile industry.
4. Availability of port, market and transport facility.
5. Coimbatore is the “Manchester of South India” for similar reasons.
Concentration of Cotton Textile Industries:
1. Distribution of Textile mills in India is concentrated in Maharashtra, Gujarat,
West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
2. In Tamil Nadu, textile mills are distributed in Erode, Tiruppur, Karur, Chennai,
Tirunelveli, Madurai, Salem and Virudhu Nagar.
3. At present, “Cotton textile industry” is the largest organised “modern industry”
in India.
2. Describe the major challenges of Indian industries.
Answer Key:
Major challenges of Indian industries :
1. Shortage and fluctation in power supply.
2. Poor access credit.
3. Non - availability of Cheap labour.
4. Non - availability of large blocks at land.
5. High rare of interac for borrowed loan.
6. Lack of technical and vocational training for employees.
7. Inappropriate living conditions near by the industrial estates.
VI. On the outline map of India mark the following.
1. Iron ore production centres.Answer Key:
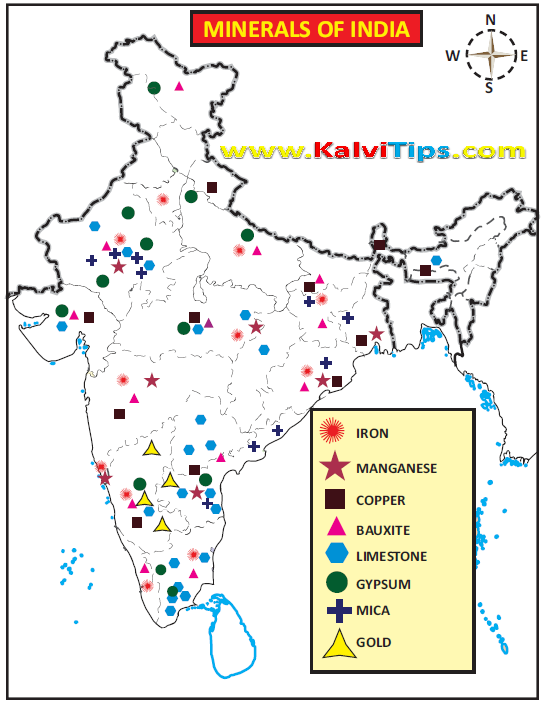
Answer Key:

3. Coal mining centres.
Answer Key:

4. Areas of cultivation of cotton.
Answer Key:

5. Iron and Steel industries.
Answer Key:










0 Comments:
Post a Comment