Tamil Nadu Board 10th Standard Social Science - Geography Unit 5: Book Back Answers and Solutions
This post covers the book back answers and solutions for Unit 5 – Geography from the Tamil Nadu State Board 10th Standard Social Science textbook. These detailed answers have been carefully prepared by our expert teachers at KalviTips.com.
We have explained each answer in a simple, easy-to-understand format, highlighting important points step by step under the relevant subtopics. Students are advised to read and memorize these subtopics thoroughly. Once you understand the main concepts, you’ll be able to connect other related points with real-life examples and confidently present them in your tests and exams.
By going through this material, you’ll gain a strong understanding of Geography Unit 5 along with the corresponding book back questions and answers (PDF format).
Question Types Covered:
- 1 Mark Questions: Choose the correct answer, Fill in the blanks, Identify the correct statement, Match the following
- 2 Mark Questions: Answer briefly
- 3, 4, and 5 Mark Questions: Answer in detail
All answers are presented in a clear and student-friendly manner, focusing on key points to help you score full marks.
All the best, Class 10 students! Prepare well and aim for top scores. Thank you!
Unit 5 : India - Population, Transport, Communication & Trade
I. Choose the correct answer.
1. The scientific study of different aspects of population is called _____.a) Cartography
b) Demography
c) Anthropology
d) Epigraphy
Answer Key:
b) Demography
2. _____ transport provides door to door services.
a) Railways
b) Roadways
c) Airways
d) Waterways
Answer Key:
b) Roadways
3. The length of the Golden Quadrilateral superhighways in India is _____.
a) 5846 km
b) 5942 km
c) 5630 km
d) 5800 km
Answer Key:
a) 5846 km
4. The National Remote Sensing Centre(NRSC) is located at ______.
a) Bengaluru
b) Chennai
c) Delhi
d) Hyderabad
Answer Key:
d) Hyderabad
5. The transport useful in the inaccessible areas is _____.
a) Roadways
b) Railways
c) Airways
d) Waterways
Answer Key:
c) Airways
6. Which of the following is associated with helicopter service?
a) Air India
b) Indian Airlines
c) Vayudoot
d) Pavan Hans
Answer Key:
d) Pavan Hans
7. The major import item of India is ______.
a) Cement
b) Jewels
c) Tea
d) Petroleum
Answer Key:
d) Petroleum
II. Match the following.
|
1
|
Border Road Organisation
|
Satellite Communication
|
|
2
|
INSAT
|
Impact of Urbanization
|
|
3
|
Mazagaon Dock
|
1955
|
|
4
|
Urban sprawl
|
Mumbai
|
|
5
|
NHAI
|
1960
|
|
1
|
Border Road Organisation
|
1960
|
|
2
|
INSAT
|
Satellite Communication
|
|
3
|
Mazagaon Dock
|
Mumbai
|
|
4
|
Urban sprawl
|
Impact of Urbanization
|
|
5
|
NHAI
|
1955
|
III. Answer the following questions briefly.
1. What is migration? State its types.Answer Key:
The movement of people across regions and territories is called migration.
The type of migration :
1. Internal migration (Within a country)
2. International migration (Between the countries)
2. Write any four advantages of railways.
Answer Key:
1. Promote national integration by bringing people together.
2. Promote trade, tourism, education etc.
3. By quick movement of perishable goods and bulky goods, railways help commercialization of agriculture.
4. Help in transporting raw materials to industries and finished goods to markets.
3. Write a note on Pipeline network transport in India.
Answer Key:
1. Pipelines provide a very convenient mode of transport to connect oil and natural gas fields refineries to the markets.
2. In the past pipelines were used to transport water to cities and industries.
3. Now solids converted into slurry can be transported through pipes.
4. Pipelines can be laid through rough terrain as well as under water.
5. As it ensures steady supply, it reduces transhipment losses and delays.
4. State the major Inland waterways of India.
Answer Key:
National Waterway 1
1. It extends between Haldia and Allahabad, measures 1620 km and includes the stretches of the Ganga-Bhagirathi-Hooghly river system.
National Waterway 2
1. This waterway includes the stretch of the Brahmaputra river between Dhubri and Sadiya, a distance of 891 km.
National Waterway 3
1. This waterway extends between Kollam and Kottapuram in the state of Kerala.
2. It is the first national waterway in the country with 24 hour navigation facilities along its entire stretch of 205 km.
5. What is communication? What are its types?
Answer Key:
1. Communication is a process that involves exchange of information, thoughts and ideas.
2. There are two types - Personal Communication and Mass communication.
6. Define “International trade”.
Answer Key:
1. International trade is trade carried on between two or more countries.
2. It is also called external trade or foreign trade. Foreign currency is involved in this trade.
7. State the merits of Roadways.
Answer Key:
1. Roadways carry goods and people to long, medium and short distances.
2. Road construction is cheap and easy to maintain.
3. Establishes easy contact between farms, fields, factories and markets.
4. Provides door to door transport services.
5. All sections of people use roadways.
IV. Distinguish between.
1. Personal communication and Mass communication.Answer Key:
|
Personal
communication
|
Mass
communication
|
|
Exchange of information between
individuals.
|
Millions of people get the
information at the same time.
|
|
Includes Post and Telegraph,
Telephone, Mobile phone, SMS, Fax, Internet etc.
|
Includes Radio, T.V. Newspaper
etc.
|
|
Enables Direct Contact.
|
Direct contact not possible.
|
|
Messages can be sent.
|
Awareness among people can be
created on national policies and programmes.
|
Answer Key:
|
Print
Media
|
Electronic
Media
|
|
Printed materials give
information.
|
Electronic gadgets give
information.
|
|
Includes Newspapers, Journals and Magazines.
|
Includes Radio, T.V. and
Internet.
|
|
Newspapers give news about
local, national and international events to the people.
|
Programmes related to education, entertainment and information
are broadcast.
|
Answer Key:
|
Roadways
|
Railways
|
|
Cost - efficient and most
universal mode of transport.
|
Main artery of the country’s
inland transport in India.
|
|
Play an important role in
carrying people and goods to short, medium and long distances.
|
Cater to the large scale
movement of people and goods and passengers.
|
|
Construction and maintenance is
cheap and easy.
|
Construction and maintenance is costly.
|
|
India has the second largest
Road network in the world.
|
India has the second largest
Road network in the world.
|
4. Waterways and Airways.
Answer key:
|
Waterways
|
Airways
|
|
The oldest and cheapest mode of transport.
|
Most modern and quickest but
costliest mode of transport.
|
|
Most suitable to carry heavy
materials to different countries.
|
Carry passengers and freight.
|
|
Environment - friendly and
affordable besides fuel - efficient.
|
Not fuel - efficient.
|
|
Inland waterways and ocean
waterways are the two types of waterways.
|
Inland waterways and ocean
waterways are the two types of waterways.
|
5. Internal trade and International trade.
Answer key:
|
Internal
trade
|
International
trade
|
|
Trade within the domestic
territory of a country.
|
Trade carried on between two or
more countries.
|
|
It is called Local trade or
Domestic trade.
|
It is called External trade or
Foreign trade.
|
|
Plays a major role in economy.
|
Plays a vital role in foreign
reserves.
|
|
Local currency is used in
transactions.
|
Foreign currency is involved in transactions.
|
V. Answer the following in a paragraph.
1. What is urbanization? Explain its problem.Answer Key:
1. Transformation of a society from Rural to urban is called ‘Urbanisation’.
2. Rural to Urban migration leads to population explosion in urban areas.
E.g.: Mumbai, Kolkata, Delhi
Problems of urbanisation:
1. It creates urban sprawl.
2. It makes overcrowding in urban centres.
3. It leads to shortage of houses in urban areas.
4. It leads to the formation of slums.
5. It increases traffic congestion in cities.
6. It creates water scarcity in cities.
7. It creates drainage problem
8. It poses the problem of solid waste management.
9. It increases the rate of crime.
2. Explain the importance of Satellite Communication in India.
Answer key:
1. Satellites are used to getting continuous and Synoptic view of larger areas.
2. Useful in weather forecasting, monitoring of natural calamities and surveillance of border areas. After the establishment of ISRO in 1969, a new era has emerged.
3. INSAT and IRS are two groups of communication.
4. ISRO (1983) is a multi - purpose system for communication, meteorological observation and other uses.
5. INSAT series are used to relay signals for T.V. Telephone and Mobile phones.
6. INSAT is also used in weather detection, internet and defence application.
7. INSAT, GSAT, KALPANA- 1, HAMSAT, EDUSAT are major communication satellites.
8. INSAT IB, launched on 30th August 1983, is the first communication satellite in INSAT series.
9. GSAT - 7A is the recent launch (Dec.19, 2018) for Communication Programs.
3. Classify and explain the roadways in India.
Answer Key:
Roadways in India:
1. Roadways is the most universal mode of transport which carry people and goods for short and long distances.
2. Roadways provide door to door transport services.
Classification:
National Highways:
1. It is the most important system of transportation connecting major cities in India.
2. They connect state capitals, ports, industrial and tourist destinations.
3. Ministry of Roadways and Highways of India is responsible for construction and maintenance of roadways.
4. The longest NH - 44 is from Srinagar in Jammu and Kashmir to Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu about 3745 k.m.
5. The shortest NH - 47A is from Ernakulam to Kochi port. (Willingdon Island - 6km.)
State Highways:
1. They connect important cities towns in a state and district Head quarters.
2. The state governments administered finance and maintain state highways.
District Roads:
1. Connect district and taluk Head quarters.
2. Public Works Department of the state maintains and constructed them.
Rural Roads: (Village Roads)
1. They provide the vital link to the rural areas.Different villages are linked to neighbouring towns.
2. They are maintained by Village Panchayats.
Border Roads:
1. Border Roads Organisation established in 1960 constructed roads in the border areas like the Northern and North Eastern Border areas.
2. Border Roads Organization has constructed world’s highest road joining Chandigarh and Leh in Ladakh.
3. This road runs at an average altitude of 4,270 meters.
Golden Quadrilateral:
1. Golden Quadrilateral 5,846 km long road of 4/6 lanes connects, India’s four metropolitan cities : Delhi-Kolkata-Chennai-Mumbai-Delhi.
2. This project was launched in 1999.
North–South and East-West Corridors:
1. North-South corridor aims at connecting Srinagar in Jammu and Kashmir with
Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu (including Kochi-Salem Spur) with 4,076km long road.
2. The East-West corridor has been planned to connect Silchar in Assam with the
port town of Porbandar in Gujarat with 3,640km of road length.
3. The two corridors intersect at Jhansi.
Express ways:
1. These are meant for speedy transport of people and frieght on multilane quality roads.
Mumbai - Pune Road
Kolkata - Dum Dum Airport Road
Durgapuram - Kolkata
Delhi - Agra - Yamuna Express Highway.
International Highways:
1. They link India with neighbouring countries. They connect India with Pakistan, Bangaldesh, Myanmar, Nepal and Bhutan.
2. World Bank aids to construct these highways.
VI. On the outline map of India mark the following.
Answer Key:
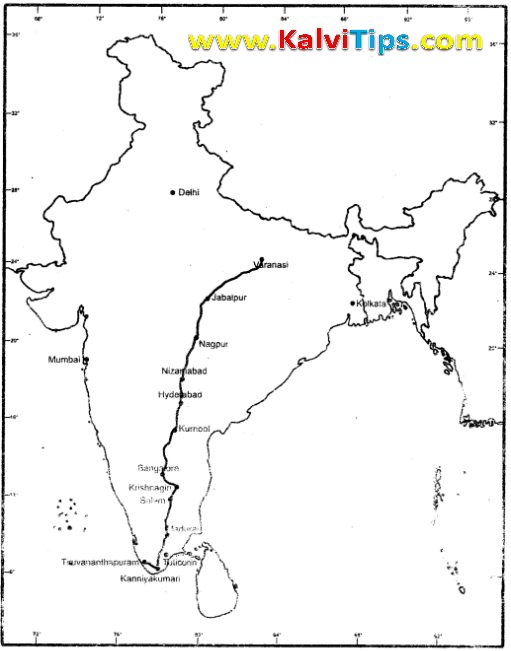
Answer Key:

Answer Key

Answer Key:

Answer Key:

Answer Key:










0 Comments:
Post a Comment