Tamil Nadu Board 10th Standard Social Science - Geography Unit 2: Book Back Answers and Solutions
This post covers the book back answers and solutions for Unit 2 – Geography from the Tamil Nadu State Board 10th Standard Social Science textbook. These detailed answers have been carefully prepared by our expert teachers at KalviTips.com.
We have explained each answer in a simple, easy-to-understand format, highlighting important points step by step under the relevant subtopics. Students are advised to read and memorize these subtopics thoroughly. Once you understand the main concepts, you’ll be able to connect other related points with real-life examples and confidently present them in your tests and exams.
By going through this material, you’ll gain a strong understanding of Geography Unit 2 along with the corresponding book back questions and answers (PDF format).
Question Types Covered:
- 1 Mark Questions: Choose the correct answer, Fill in the blanks, Identify the correct statement, Match the following
- 2 Mark Questions: Answer briefly
- 3, 4, and 5 Mark Questions: Answer in detail
All answers are presented in a clear and student-friendly manner, focusing on key points to help you score full marks.
All the best, Class 10 students! Prepare well and aim for top scores. Thank you!
Unit 2: Climate and Natural Vegetation of India
I. Choose the correct answer.
1. Western disturbances cause rainfall in _____.a) Tamilnadu
b) Kerala
c) Punjab
d) Madhya Pradesh
Answer Key:
c) Punjab
2. _____ helps in quick ripening of mangoes along the coast of Kerala and Karnataka.
a) Loo
b) Norwester
c) Mango showers
d) Jet stream
Answer Key:
c) Mango showers
3. _____ is a line joining the places of equal rainfall.
a) Isohyets
b) Isobar
c) Isotherm
d) Latitudes
Answer Key:
a) Isohyets
4. Climate of India is labelled as _____.
a) Tropical humid
b) Equatorial Climate
c) Tropical Monsoon Climate
d) Temperate Climate
Answer Key:
c) Tropical Monsoon Climate
5. The monsoon forests are otherwise called as _____.
a) Tropical evergreen forests
b) Deciduous forests
c) Mangrove forests
d) Mountain forests
Answer Key:
b) Deciduous forests
6. Sesahachalam hills, a Biosphere reserve, is situated in _____.
a) Tamil Nadu
b) Andhra Pradesh
c) Madhya Pradesh
d) Karnataka
Answer Key:
b) Andhra Pradesh
7. _____ is not a part of the world network biosphere reserves of UNESCO.
a) The Nilgiris
b) Agasthiyamalai
c) Great Nicobar
d) Kachch
Answer Key:
d) Kachch
II. Match the following.
|
1
|
Sundarbans
|
Desert and semi - desert
vegetation
|
|
2
|
Biodiversity hotspot
|
October - December
|
|
3
|
North east monsoon
|
Littoral forest
|
|
4
|
Tropical thorn forests
|
West Bengal
|
|
5
|
Coastal forests
|
The Himalayas
|
|
1
|
Sundarbans
|
West Bengal
|
|
2
|
Biodiversity hotspot
|
The Himalayas
|
|
3
|
North east monsoon
|
October - December
|
|
4
|
Tropical thorn forests
|
Desert and semi - desert vegetation
|
|
5
|
Coastal forests
|
Littoral forest
|
III. Consider the given statement and choose the correct option from the given below ones.
1. Assertion (A) : The Himalayas acts as a climatic barrier.Reason (R) : The Himalayas prevents cold winds from central Asia and keep the Indian Sub continent warm.
a) Both (A) and (R) are true: R explains A
b) Both (A) and (R) are true: R does not explain A
c) (A) is true (R) is false
d) (A) is false (R) is true
Answer Key:
a) Both (A) and (R) are true: R explains A
IV. Choose the inappropriate answer.
1. Tidal forests are found in and around ____. a) Desert
b) The deltas of Ganga and Brahmaputra
c) The delta of Godavari
d) The delta of Mahanadhi
Answer Key:
a) Desert
2. Climate of India is affected by___.
a) Latitudinal extent
b) Altitude
c) Distance from the sea
d) Soil
Answer Key:
d) Soil
V. Answer briefly.
1. List the factors affecting climate of India.Answer Key:
1. Latitude, Altitude, Distance from the sea, Monsoon winds, Relief features and Jet streams.
2. What is meant by ‘normal lapse rate’?
Answer Key:
1. When the altitude increases the temperature decreases.
2. The rate of decrease of temperature is 6.5ºC for every 1000mt of ascent.
3. This is called ‘Normal lapse rate’.
3. What are ‘jet streams’?
Answer Key:
1. Jet streams are the fast moving winds blowing in a narrow zone in the upper atmosphere.
2. The jet stream theory states that the onset of South - West Monsoon is driven by the shift of the sub - tropical westerly jet from the plains of India towards the Tibetan plateau.
3. Tropical depressions are caused by the easterly jet streams both during Southwest Monsoon and its retreat.
4. Write a short note on ‘Monsoon wind’.
Answer Key:
1. Monsoon wind is the most dominant factor which affects the climate in India.
2. The word monsoon is derived from the Arabic word “Mausim” which means “Season”.
3. India is influenced by the seasonal reversal winds.
4. These winds blow from the southwest to northeast during summer and from Northeast to Southwest in the winter.
5. Name the four distinct seasons of India.
|
Four Distinct Seasons of India:
|
|
|
Winter Season
|
January - February
|
|
Summer Season
|
March - May
|
|
South – West Monsoon (Rainy Season)
|
June - September
|
|
North – East Monsoon Season
|
October - December
|
Answer Key:
1. Prior to the onset of the South West Monsoon, the temperature in North India reaches up to 46ºC.
2. This sudden approach of monsoon wind over South India with lightning and thunder is called ‘break’ or ‘burst of monsoon’.
7. Name the areas which receive heavy rainfall.
Answer Key:
1. The Western Coast
2. Assam
3. South Meghalaya
4. Tripura
5. Nagaland
6. Arunachal Pradesh
8. State the places of mangrove forests in India.
Answer Key:
1. The Ganga - Brahmaputra delta.
2. Mahanadi, Godavari and Krishna deltas.
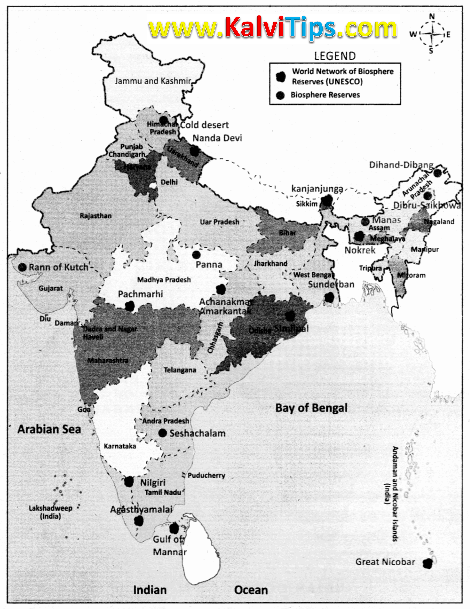
9. Write any five biosphere reserves in India.
Answer Key:
1. Agasthyamalai - Kerala
2. Great Nicobar - Andaman & Nicobar
3. Gulf of Mannar - Tamil Nadu
4. Simlipal - Odisha
5. The Nilgris - Tamil Nadu
VI. Distinguish between.
1. Weather and Climate.Answer Key:
|
Weather
|
Climate
|
|
Refers to the state of
atmosphere at a given point of time.
|
It is accumulation of seasonal
weather events over a period of 30 - 35 years.
|
|
Short time condition.
|
Long time condition.
|
|
Varies constantly.
|
Does not vary constantly.
|
|
Its a study in meteorology.
|
Its a study in climatology
|
Answer Key:
|
Tropical
Evergreen Forest
|
Deciduous
Forest.
|
|
Found in areas with rainfall
above 200 cm. They do not shed their
leaves.
|
Found in areas with rainfall
between 100 - 200 cm. They shed their leaves.
|
|
Annual temperature is more than
22°C.
|
Annual temperature is about 27°C.
|
|
Humidity exceeds 70%.
|
Relative humidity ranges from 60
- 70 %.
|
|
Contain Rubber, Mahogany, ebony,
rosewood trees.
|
Teak, Sal, Sandalwood and Bamboo
trees are found.
|
|
They are found in Maharashtra, Karnataka
etc.
|
They are found in Uttar Pradesh,
Bihar etc.
|
Answer Key:
|
North
East Monsoon
|
South
West Monsoon
|
|
Retreats from North India and
blows towards Bay of Bengal.
|
Onset takes place over the
southern tip of the country. It advances along the
Konkan coast.
|
|
It is associated with the North
- easterly wind system.
|
It is influenced by the global
phenomenon ELNINO.
|
|
Gives only 25% rainfall in
India.
|
India gets 75% rain due to this.
|
|
Gives rain to Coromandel Coast.
|
Gives rain to West Coastal
Plain.
|
|
Season : October - December.
|
Season : June - September.
|
VII. Give reasons.
1. India has a tropical monsoon climate.Answer Key:
1. Most of India lies in the tropical belt and the climate is influenced by monsoon
winds which blow in the tropics. [20ºN and 20ºs]
2. So, India has a tropical monsoon climate.
2. Mountains are cooler than the plains.
Answer Key:
1. When the altitude increases the temperature decreases.
2. Temperature decreases at the rate of 6.5ºC per 1000m ascent.
VIII. Answer in detail.
1. Write about South West Monsoon.Answer Key:
South West Monsoon: (June to September)
1. The Southwest Monsoon is the most significant feature in Indian climate.
2. Normally the Southwest monsoon sets in over the southern tip of the country in June.
3. It advances to the Konkan region and covers the entire whole country by 15th July.
4. It is influenced by the global phenomenon like ELNINO.
5. Before its onset the temperature in North reaches upto 46ºC.
6. The sudden approach of Monsoon is called ‘Break (or) Burst of monsoon’.
7. The monsoon wind divides into two branches and blows from the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
Arabian Sea Branch:
1. It gives heavy rainfall to the West Coast as it is located windwardside.
2. The other part advances to North.
3. It is obstructed by the Himalayas and the North gets heavy rain.
4. As the Aravalli range is parallel to the wind direction, the North Eastern parts
do not get rain.
Bay of Bengal Branch:
1. The wind from Bay of Bengal branch moves towards NorthEast India and Myanmar.
2. This wind is trapped by a chain mountains Garo, Kashi etc.
3. They bring heavy rain.
4. Later the winds travel towards west and become dry giving scanty rainfall.
5. Overall about 75% of rainfall in India is received due to this monsoon.
2. Describe the forests of India.
Answer Key:
Based on the climate, soil and landforms, the forests in India can be classified as
follows :
Tropical Evergreen forests - Tropical Deciduous forests - Tropical Dry forests -
Mountain forests - Alpine forests - Tidal forests.
Tropical Evergreen forests:
1. They are found in areas where the annual rainfall is above 200 cm.
2. They cover - western ghats in Maharashtra and Karnataka, Kerala, Assam, West Bengal and Northeastern states.
3. Rubber, Mahogamy, ebony, rosewood, coconut, bamboo and palm trees are abundant.
Tropical Deciduous forests: (Monsoon forest)
1. They are found in areas with annual rainfall of 100 - 200 cm, shed their leaves in summer.
2. Sub - Himalayan range, Great plains, Central India and South India come under this.
3. Sandalwood, rosewood, teak, sal, kusum, Mahua, Palas, Amla, Padauk and Bamboo trees grow here.
Tropical Dry forests:
1. These are found in areas with annual rainfall of 50 - 100 cm.
2. East Rajasthan, Haryana, Punjab, Western Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Eastern Maharashtra, East TamilNadu come under this. Mahua, banyan, amaltas, palas, haldu, bamboo, babool and khair trees are found here.
Mountain forests (or) Montane forest:
1. Areas under moderate rainfall, and found in the altitude at 1200 - 2400 m.
2. Mountain slopes in N.E. States, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand come under this category.
3. Sal, Oak, Laurel, Amra, Chestnut, Cinnamon are the main trees found.
Alphine forests:
1. These the forests are found in the altitude 2400 m.
2. Coniferous trees, Oak, Silver, Fir, Pine, Juniper grow here.
Tidal forests:
1. Ganga - Brahmaputra, Godavary, Mahanadi, Krishna river deltas come under this also called Mangrove forests.
2. Ganga - Brahmaputra delta has the largest tidal forest in the world. (Sunderban Delta)
IX. Map.
1. Direction of South West Monsoon wind.Answer Key:

Answer Key:

Answer Key:

Answer Key:

Answer Key:

Answer Key:









0 Comments:
Post a Comment