Tamil Nadu Board 10th Standard Social Science - Geography Unit 3: Book Back Answers and Solutions
This post covers the book back answers and solutions for Unit 3 – Geography from the Tamil Nadu State Board 10th Standard Social Science textbook. These detailed answers have been carefully prepared by our expert teachers at KalviTips.com.
We have explained each answer in a simple, easy-to-understand format, highlighting important points step by step under the relevant subtopics. Students are advised to read and memorize these subtopics thoroughly. Once you understand the main concepts, you’ll be able to connect other related points with real-life examples and confidently present them in your tests and exams.
By going through this material, you’ll gain a strong understanding of Geography Unit 3 along with the corresponding book back questions and answers (PDF format).
Question Types Covered:
- 1 Mark Questions: Choose the correct answer, Fill in the blanks, Identify the correct statement, Match the following
- 2 Mark Questions: Answer briefly
- 3, 4, and 5 Mark Questions: Answer in detail
All answers are presented in a clear and student-friendly manner, focusing on key points to help you score full marks.
All the best, Class 10 students! Prepare well and aim for top scores. Thank you!
Unit 3: India - Agriculture
I. Choose the correct answer.
1. The soil which is rich in iron oxides is _____ soil.a) Alluvial
b) Black
c) Red
d) Alkaline
Answer Key:
c) Red
2. Which of the following organization has divided the Indian soils into 8 major groups?
a) Indian Council of Agricultural Research
b) Indian Meteorological Department
c) Soil Survey of India
d) Indian Institute of Soil Science
Answer Key:
a) Indian Council of Agricultural Research
3. The soils formed by the rivers are _____.
a) Red soils
b) Black soils
c) Desert soils
d) Alluvial soils
Answer Key:
d) Alluvial soils
4. _____ is the highest gravity dam in India.
a) Hirakud dam
b) Bhakra Nangal dam
c) Mettur dam
d) Nagarjuna Sagar dam
Answer Key:
b) Bhakra Nangal dam
5. _____ is a cash crop.
a) Cotton
b) Wheat
c) Rice
d) Maize
Answer Key:
a) Cotton
6. Black soils are also called as _____.
a) Arid soils
b) Saline soils
c) Regur soils
d) Mountain soils
Answer Key:
c) Regur soils
7. The longest dam in the world is _____.
a) Mettur dam
b) Kosi dam
c) Hirakud dam
d) Bhakra-Nangal dam
Answer Key:
c) Hirakud dam
8. Which crop is called as “Golden Fibre” in India?
a) Cotton
b) Wheat
c) Jute
d) Tobacco
Answer Key:
c) Jute
II. Consider the given statements and choose the right option given below.
1. Assertion (A) : Horticulture involves cultivation of fruits, vegetables, and flowers.Reason (R) : India ranks first in the world in the production of mango, banana, and citrus fruits.
a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
b) Both (A) and (R)are true: (R) does not explain (A)
c) (A) is correct (R) is false
d) (A) is false (R) is true
Answer Key:
(c) (A) is correct (R) is false
2. Assertion (A) : Alluvial soil is formed by the deposition of eroded and decayed materials brought by the rivers.
Reason (R) : Paddy and wheat are grown well in this soil.
a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
b) Both (A) and (R)are true and (R) does not explain (A)
c) (A) is correct (R) is false
d) (A) is false (R) is true
Answer Key:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
III. Pick the odd one out.
1. a) Wheatb) Rice
c) Millets
d) Coffee
Answer Key:
d) Coffee
2. a) Khadar
b) Bhangar
c) Alluvial soil
d) Black soil
Answer Key:
d) Black soil
3. a) Inundation canals
b) Perennial canals
c) Tanks
d) Canals
Answer Key:
c) Tanks
IV. Match the following.
|
1
|
Sugar bowl of India
|
Mahanadi
|
|
2
|
Coffee
|
Golden revolution
|
|
3
|
Tehri
|
Karnataka
|
|
4
|
Hirakud
|
Uttar Pradesh and Bihar
|
|
5
|
Horticulture
|
Highest dam in India
|
|
1
|
Sugar bowl of India
|
Uttar Pradesh and Bihar
|
|
2
|
Coffee
|
Karnataka
|
|
3
|
Tehri
|
Highest dam in India
|
|
4
|
Hirakud
|
Mahanadi
|
|
5
|
Horticulture
|
Golden revolution
|
V. Answer in brief.
1. Define soil.Answer Key:
1. Soil is one of the most important resources.
2. Soil is the uppermost layer of the land surface.
3. It is composed of minerals, organic matter, living organisms, air and water.
4. It is formed by weathering of rocks.
2. Name the types of soil found in India.
Answer Key:
Types of soil found in India are :
1. Alluvial Soil
2. Black Soils
3. Red Soils
4. Laterite Soils
5. Forest and Mountain Soils
6. Arid and Desert Soils
7. Saline and Alkaline Soils
8. Peaty and Marshy Soils.
3. State any two characteristics of black cotton soil.
Answer Key:
1. It contains carbonates of calcium and magnesium, iron, aluminium, lime and magnesia. It is rich in potash, lime, aluminium, calcium and magnesium.
2. Nitrogen, Phosphoric acid and humus are in less quantity.
3. Moisture retention is high. Cotton grows well.
4. Define Agriculture.
Answer key:
Agriculture is defined as the process of producing food for people, fodder for cattle - fiber and many other desired products by the cultivation of certain plants and raising of domesticated animals (livestock).
5. State the types of agriculture practices in India.
Answer Key:
Types of agriculture practices in India :
1. Subsistence Farming
2. Shifting Agriculture
3. Intensive farming
4. Dry farming
5. Mixed farming
6. Terrace farming.
6. Name the seasons of agriculture in India?
Answer Key:
The “three” agriculture seasons of India are :
1. Kharif season (June - September)
2. Rabi season (October - March)
3. Zaid season (April - June)
7. Mention the plantation crops of India.
Answer Key:
1. Coffee
2. Tea
3. Rubber
4. Spices
8. Write a brief note on the categories of fisheries in India?
Answer Key:
There are two types of fishing.
Marine or sea fisheries :
1. It includes coastal, off - shore and deep sea fishing.
2. It is done mainly on the continental shelves.
3. Kerala is famous for marine fisheries.
Inland or Fresh water fisheries :
1. Rivers, lakes, ponds, canals and reservoirs are the sources of fresh water fishing.
2. They contribute 50% of fish products in the country.
3. Andhra Pradesh leads in it.
VI. Give reasons.
1. Agriculture is the backbone of India.Answer Key:
1. Agriculture employs more than 50% population in India.
2. It accounts for 25% of national income.
2. Rain water harvesting is necessary.
Answer Key:
1. There is only seasonal rain in India.
2. It is not uniform and highely erratic.
3. A lot of rain water drains into the sea.
4. To Augment water supply throughout the year, Rain Water Harvesting is necessary.
VII. Distinguish between the following.
1. Rabi and Kharif crop seasons.Answer Key:
|
Rabi Season
|
Kharif Season
|
|
From October to March
|
From June to September.
|
|
Wheat, Gram, Rapeseeds, Mustard,
and Barley cultivated in Northern states.
|
Rice, Cotton, Bajra, Maize and
Jowar are cultivated in North.
|
|
Rice, Maize, Ragi, Jowar and
Groundnut are cultivated in Southern states.
|
Rice, Ragi, Maize, Jowar and
Ground nut are cultivated in Southern states
|
Answer Key:
|
Inundation canal
|
Perennial canal
|
|
Water is taken out directly from
rivers without construction dams or barrage.
|
Developed from Perennial rivers
by constructing dams or barrages to regulate the flow of water.
|
|
Useful for diversion of flood
water from rivers.
|
Useful for irrigation.
|
|
Operational only during rainy
season.
|
Operational throughout the year.
|
Answer Key:
|
Marine fishing
|
Inland fishing
|
|
Includes coastal, off - shore
and deep sea fishing.
|
Includes fishing in rivers,
canals, reserviors, ponds.
|
|
Saline water fishing.
|
Fresh water fishing.
|
|
Kerala leads in this.
|
Andhra Pradesh leads in it.
|
4. Alluvial soils and Black soils.
Answer Key:
|
Alluvial soils
|
Black soils
|
|
Formed from sediments deposited
by rivers.
|
Derived from basalts of Deccan plateau.
|
|
Rich in potash, phosphoric acid,
lime and carbon compounds.
|
Rich in potash, lime, aluminium.
|
|
Found in Northern river valleys.
|
Found in Deccan plateau region.
|
|
Rice, wheat, sugarcane, oil
seeds are grown in these soils.
|
Cotton, millets, tobacco,
sugarcane are grown in these soils.
|
VIII. Answer in a paragraph.
i) Alluvial soil
Formation:
Chemical Properties:
1. Rich in potash, phosphoric acid, lime and carbon compounds. poor in Nitrogen.
Distribution:
1. Ganga and Brahmaputra river valleys.
2. Plains of Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, West Bengal and Bihar. River mouth
of East Coast.
Colour and Nature:
1. Sandy - loam - silky - clay light coloured (Khadar) Dark colour (Bhangar)
ii) Black soil:
Formation:
Derived from basalts of Deccan trap.
Chemical Properties :
Contains Calcium and Magnesium carbonates, High in aluminium, Lime and Magnesia. Poor in Nitrogen, Phosphoric acid and humus.
Distribution :
Maharashtra and Malwa Plateau, Kathiawar Peninsula, Telangana, Rayala Seema (Andhra Pradesh), Northern Karnataka.
Colour and Nature :
Sticky, high moisture retention, black colour due to presence of iron and titanium.
iii) Red soil :
Formation :
Decomposition of ancient crystaline rocks like granites and gneisses.
Chemical Properties :
Rich in iron and magnesium, poor in Nitrogen and Phosphoric acid.
Nature :
Light texture, porous friable presence of limited soluble salts.
Distribution :
Kerala, TamilNadu, Karnataka, Chota Nagpur, plateau.
Colour and Nature :
Light texture, Porous - limited salts.
iv) Laterite soil :
Formation :
By process of leaching.
Chemical Properties :
Composed of hydrated oxides of iron and aluminium.
Colour and Nature :
More acidic in higher areas, poor moisture retention.
Distribution :
Assam, Kerala, Karnataka and Odisha.
v) Forest and Mountain soil :
Formation :
Due to mechanical weathering caused by rain and temperature.
Chemical Properties :
Poor in potash, lime and phosphorus.
Distribution :
Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Eastern and Western ghats.
Colour and Nature :
Light, Sandy, thin and rich in humus.
2. What is Multipurpose projects and write about any two Multipurpose projects of India.
Answer Key:
Multipurpose Projects :
1. It is a project of scientific management of water for various purposes.
2. Dams are constructed across rivers for the purpose of irrigation.
3. Hydro - power generation, drinking water supply, industrial purpose, controlling floods, development of fisheries navigation etc. are the other purposes of dams.
4. As these projects serve several purposes, they are called multi - purpose projects.
5. Majority of multi - purpose projects are combination of Irrigation and Hydro - power because they are the major aims of the projects.
Bhakra - Nangal Project :
1. Constructed across Sutlej river. It is the highest gravity dam in the world.
2. Punjab, Haryana and Rajasthan are benefitted.
3. It irrigates 52609 sq kms.
4. It produces 1500 M.W. of hydro power.
Hirakud Project :
1. Constructed across river Mahanadi.
2. It is the longest dam in the world.
3. Odisha is benefitted.
4. It irrigates 1,41,600 sq. kms.
5. It produces 347.5 M.W. of Hydro power.
3. Bring out the characteristics of Intensive and Mixed farming.
Answer Key:
Intensive farming :
1. It is an agricultural intensification and mechanization system.
2. Heavy use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers maximise yield from available land.
Mixed farming :
1. Mixed farming is defined as a system of farming which includes crop production, raising livestock, poultry, fisheries, bee keeping etc. to sustain and satisfy as many needs of the farmer as possible.
4. Examine the geographical conditions favourable for the cultivation of rice and wheat.
Answer Key:
Rice :
1. India is the second largest producer of rice in the world after China.
2. It is an indigenous tropical food crop.
3. It needs a mean temperature of 24ºC and 150 cm annual rainfall.
4. Deep fertile clay soil or loamy soils is needed for rice cultivation. River deltas are suitable for rice cultivation.
5. Rice cultivation needs huge supply of cheap labour.
6. India follows (i) Broad Casting, (ii) Ploughing (or) Drilling and (iii) Transplanting methods in rice cultivation.
7. West Bengal, (1st in India), Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, TamilNadu, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Odisha, Chattisgarh, etc. and Haryana are major producers of rice.
8. (CR Dhan 205, AR Dhan 306, CRR 451 are some of the High Yielding Variety (HYV) seeds.)
Wheat :
1. It is the second most important food crop after rice.
2. It accounts for 22% of total area and 34% of total production of food grains.
3. It requires 10 - 15ºC at sowing and 20 - 25ºC at the time of ripening.
4. Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh account for over 85% of India’s wheat production.
5. Parts of Maharashtra and Gujarat also produce wheat.
IX. Hot questions.
1. Can you imagine a world without agriculture?Answer Key:
1. No, we cannot imagine a world without agriculture.
2. It is the backbone of our country.
3. It employs 50% of workers and contributes 18% to the economy.
4. Food is vital for survival.
5. There will be no food without agriculture.
2. Can you give solutions for the prevailing water disputes in South India?
Answer Key:
1. South Indian rivers depend on rain.
2. So it is essential that all the rain water is preserved without any waste.
3. Dams should be constructed across rivers to store rain water.
4. All the states using the rivers should come to an understanding to share the river water as per their need without any dispute.
5. If the Peninsular rivers are connected with the North Indian Perennial rivers, the problem can be solved.
6. The height of the dams should be raised to increase the storage capacity.
7. Cleaning and repairing of tanks to be taken up to prevent wastage of water.
X. Map exercise.
1. Demarcate the major tracts of alluvial soils.Answer Key:
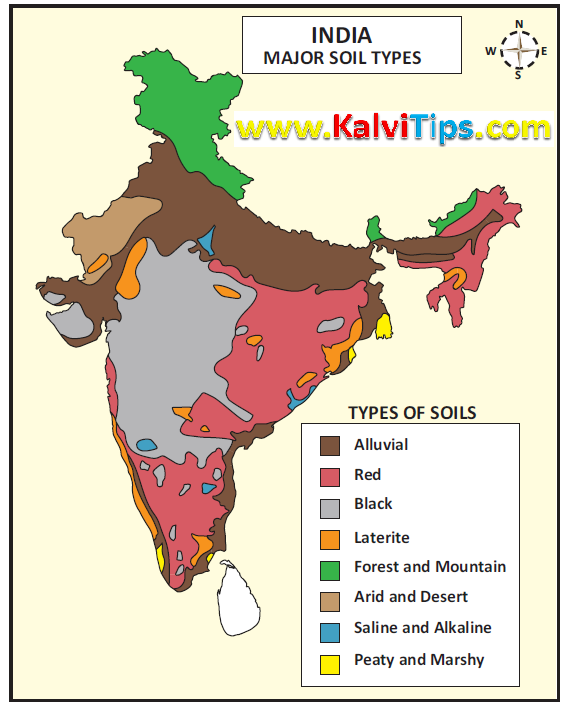
Answer Key:

Answer Key:

Answer Key:

Answer Key:

Answer Key:

Answer Key:

Answer Key:
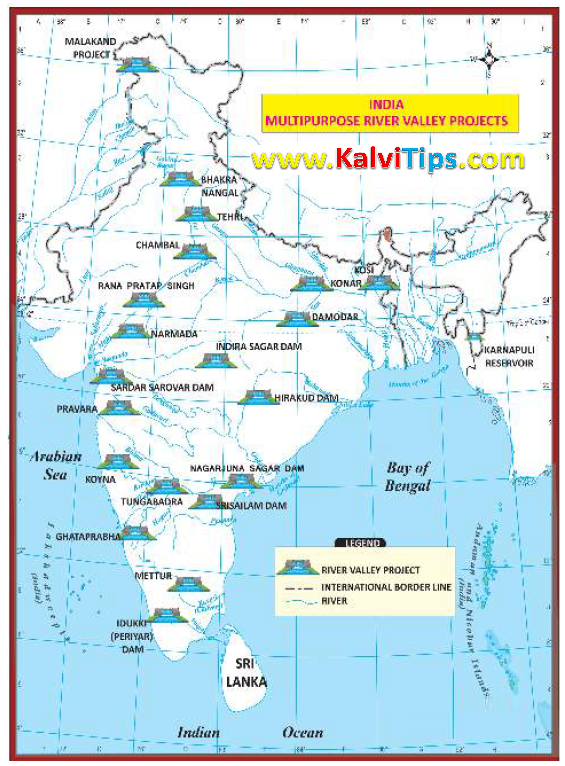









0 Comments:
Post a Comment