Plus Two / 12th Physics - Book Back Answers - Unit 1 - English Medium
Tamil Nadu Board 12th Standard Physics - Unit 1: Book Back Answers and Solutions
This post covers the book back answers and solutions for Unit 1 from the Tamil Nadu State Board 12th Standard Physics textbook. These detailed answers have been carefully prepared by our expert teachers at KalviTips.com.
We have explained each answer in a simple, easy-to-understand format, highlighting important points step by step under the relevant subtopics. Students are advised to read and memorize these subtopics thoroughly. Once you understand the main concepts, you’ll be able to connect other related points with real-life examples and confidently present them in your tests and exams.
By going through this material, you’ll gain a strong understanding of Unit 1 along with the corresponding book back questions and answers (PDF format).
Question Types Covered:
- 1 Mark Questions: Choose the correct answer, Fill in the blanks, Identify the correct statement, Match the following
- 2 Mark Questions: Answer briefly
- 3, 4, and 5 Mark Questions: Answer in detail
All answers are presented in a clear and student-friendly manner, focusing on key points to help you score full marks.
All the best, Class 12 students! Prepare well and aim for top scores. Thank you!
I. Multiple choice questions.
1. Two identical point charges of magnitude –q are fixed as shown in the figure below. A third charge +q is placed midway between the two charges at the point P. Suppose this charge +q is displaced a small distance from the point P in the directions indicated by the arrows, in which direction(s) will +q be stable with respect to the displacement?
(a) A1
and A2
(b) B1 and B2
(c) both directions
(d) No stable
Answer Key:
(b) B1 and B2
2. Which charge configuration produces a uniform electric field?
(a) point charge
(b) uniformly charged infinite line
(c) uniformly charged infinite plane
(d) uniformly charged spherical shell
Answer Key:
(c) uniformly charged infinite plane
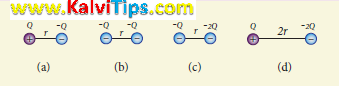
3. What is the ratio of the charges for the following electric field line pattern?
(a)
(b)
(c) 5
(d)
Answer Key:
(d)
4. An electric dipole is placed at an alignment angle of
30° with an electric field of 2 × 105 NC-1. It
experiences a torque equal to 8 Nm. The charge on the dipole if the dipole
length is lcm is
(a) 4 mC
(b) 8 mC
(c) 5 mC
(d) 7 mC
Answer Key:
(b) 8 mC
Hint:
T = PE sin θ
T = (q × 21)E sin30°
q = (q × 10-2) ×
q = 8 × 10-2c
5. Four Gaussian surfaces are given below with charges inside each Gaussian surface. Rank the electric flux through each Gaussian surface in increasing order.
(a) D < C < B < A
(b) A < B = C < D
(c) C < A = B < D
(d) D > C > B > A Answer Key:
(a) D < C < B < A
Hint:
flux depends on charge
6. The total electric flux for the following closed surface which is kept inside water.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer Key:
(b)
ϕ=q40∈∘
7. Two identical conducting balls having positive charges q1 and q2
are separated by a center to center distance r. If they are made to touch each
other and then separated to the same distance, the force between them will be
(a) less than before
(b) same as before
(c) more than before
(d) zero
Answer Key:
(c) more than before
Hint:
F=Kq1q2r2
F=K(q1q22)(q1q12)r2
F'>F
8. Rank the electrostatic potential energies for the given system of charges in
increasing order:
(a) 1
= 4 < 2 < 3
(b) 2 = 4 < 3 < 1
(c) 2 = 3 < 1 < 4
(d) 3 < 1 < 2 < 4
Answer Key:
(a) 1 = 4 < 2 < 3
Hint:
U=Kq1q1r
(i) U=-KQ2r
(ii) U=KQ2r
(iii) U=K2Q2r
(iv) U=-K2Q22r=-KQ2r
9. An electric field E→ = 10 × Î exists in a certain region of space. Then the
potential difference V = Vo – VA, where Vo is
the potential at the origin and VA is the potential at x = 2 m is:
(a) 10 V
(b) -20 V
(c) +20 V
(d) -10 V
Answer Key:
(c) +20 V
Hint:
E = -dvdx
dv = E.dx = l0x = 10 × 2
dv = 20 V
10. A thin conducting spherical shell of radius R has a charge Q which is uniformly
distributed on its surface. The correct plot for electrostatic potential due to
this spherical shell is
Hint:
In a spherical shell, the electric field inside is zero. But the electric
potential is constant.
V=q4π∈∘r as distance increases its potential decrease
non-linearly.
11. Two points A and B are maintained at a potential of 7 V and -4 V respectively.
The work done in moving 50 electrons from A to B is
(a) 8.80 × 10-17 J
(b) -8.80 × 10-17 J
(c) 4.40 × 10-17 J
(d) 5.80 × 10-17 J
Answer Key:
(a) 8.80 × 10-17 J
Hint:
WA→B = (VA – VB)q
=(7+4)ne
= 11 × 50 × 1.6 × 10-19
=8.8 × 10-17
12. If the voltage applied on a capacitor is increased from V to 2V, choose the correct
conclusion.
(a) Q remains the same, C is doubled
(b) Q is doubled, C doubled
(c) C remains the same, Q doubled
(d) Both Q and C remain the same
Answer Key:
(c) C remains the same, Q doubled
Hint:
q2q1=C(2V)CV
Q2=2Q1
13. A parallel plate capacitor stores a charge Q at a voltage V. Suppose the area of the parallel plate capacitor and the distance between the plates are each doubled then which is the quantity that will change?
(a) Capacitance
(b) Charge
(c) Voltage
(d) Energy density
Answer Key:
(d) Energy density
14. Three capacitors are connected in a triangle as shown in the figure. The equivalent capacitance between points A and C is
(a) 1 μF
(b) 2 μF
(c) 3 μF
(d) 14 μF
Answer Key:
(b) 2 μF
Hint:15. Two
metallic spheres of radii 1 cm and 3 cm are given charges of -1 × 10-2
C and 5 × 10-2 C respectively. If these are connected by a
conducting wire, the final charge on the bigger sphere is
(a) 3 × 10-2 C
(b) 4 × 10-2 C
(c) 1 × 10-2 C
(d) 2 × 10-2 C
Answer Key:
(a) 3 × 10-2 C
Hint:
Total charge Q = q1 + q2 = 4 × 10-2 C
charge on bigger sphere,
q2 = Q(r2r1+r2)
= 4 × 10-2 ×34
q2 = 3 × 10-2 C
II. Short answer questions.
1. What is meant by quantisation of charge?
Answer key:
The
charge q on any object is equal to an integral multiple of fundamental unit of charge
e. This is called quantisation of electric charge. Charge of electron = - 1.6
X 10-19 C .
q=ne
n
is any integer (0 , + 1, +
2, + 3…)
This
is called quantisation of charge.
2. Write down the Coulomb’s law in vector form and mention what each term represents.
Answer Key:
Coulomb’s law states that, Electrostatic force is directly proportional to the product of the magnitude of the point charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between two point charges.
F→21=Fq1q2r2r^12
F21 = Force on point charge q2 exerted
by another point charge q1
q1 q2 = Point charges
r12 = Unit vector
3.What are the differences between Coulomb force and
gravitational force?
Answer Key:
|
S.No
|
Coulomb
Force
|
Gravitational
Force
|
|
1
|
It
may be attractive or repulsive.
|
It
is always attractive in nature.
|
|
2
|
It
depends upon medium.
|
It
does not depend upon the medium.
|
|
3
|
It
is always greater in magnitude.
K=9x109
Nm2 C-2
|
It
is lesser than coulomb force.
G=6.67x10-11
Nm2 Kg2.
|
4. Write short note on superposition principle.
Answer Key:
When a number of charges are interacting the total force of a given charge is the vector sum of the individual forces exerted on the given charge by all the other charges.
F→1tot=F→12+F→13+F→14...+F→1n
F→1tot=F{q1q2r212r^21+q1q2r312r^31+...q1qnrn12r^n1}
5. Define electric field.
Answer Key:
The electric field at the point P at a distance r from
the point charge q is the force
experienced by a unit charge .
E→=F→q0=kqr2r^=14π∈0qr2r^
SI unit: NC-1
6. What is meant by “electric field lines”?
Answer key:
Electric field vectors are visualized by the concept of electric field lines.
They form a set of continuous lines which represent the electric field in some region of space visually.
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
7. The electric field lines never intersect . Justify.
Answer Key:
If some charge is placed in the intersection point , then it has to move in two different directions at the same time which is physically impossible. Hence , electric field lines do not intersect.
8. Define electric dipole . Give the expression for the magnitude of its electric dipole moment and the direction.
Answer Key:
Electric diapole:
Two equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance constitute an electric dipole.
P→=qr→++(-q)r→
Magnitude of the electric dipole:
Magnitude of the electric dipole moment is equal to the product of the magnitude of one of the charges and the distance between them.
P→=2qa
9. Write the general definition of electric dipole moment for a collection of point charge.
Answer Key:
The electric dipole moment for a collection of n point charges is given by where r→i is the position vector of charge qi from the origin.
P→=∑i=1nqir→i
10. Define "electrostatic potential"?.
Answer Key:
Electric potential at a point P is equal to the work done force to bring unit positive charge with constant velocity from infinity to the point P in the region of the external electric field.
Vp=-∫∞pE→.dr→
11. What is an Equi-potential surface ?
Answer Key:
An equipotential surface is a surface on which all the points are at the same electric potential.
12. What are the properties of an equipotential surface ?
Answer Key:
1. The work done to move a charge q between any two points A and B, W = q (VB – VA).
2. If the points A and B lie on same equipotential surface Work done is zero because VA = VB
3. The electric field is always normal to an equipotential surface.
13. Give the relation between electric field and
electric potential.
Answer Key:
1. Consider a positive charge q kept fixed at the origin. 2. To move a unit positive charge by a small distance dx towards q in the electric field E, the work done is given by dW = −E dx.
3. The minus sign implies that work is done against the electric field.
4. This work done is equal to electric potential difference. Therefore,
dW = dV.
(or) dV = −E dx
Hence E=-dVdx
14. Define electrostatic potential energy.
Answer Key:
Electric potential energy is defined as the work done in bringing the various charges to their respective positions from infinitely large mutual separation.
15. Define electric flux.
Answer Key:
The number of electric field lines crossing a given area kept normal to the electric field lines is called electric flux.
ΦE=E→.A→=EAcosθ
16. What is meant by electrostatic energy density?
Answer Key:
The energy stored per unit volume of space is defined electrostatic energy density.
UE=UVolume=12∈∘E2
U – electrostatic potential energy
E – electric field
∈∘ – permittivity of free space
17. Write a short note on electrostatic shielding.
Answer Key:
The phenomenon of protecting a region of space from any external electric field is called as electrostatic shielding .
Consider a cavity inside the conductor whatever the charges at the surfaces and whatever the electrical disturbances outside, the electric field inside cavity is zero.
Ex: Faraday Cage
18. What is Polarisation?
Answer Key:
Polarisation is defined as the total dipole moment per unit volume of the dielectric.
p→=χeE→ext
χe= electric susceptibility
19.What is dielectric strength ?
Answer Key:
The maximum electric field the dielectric can
withstand before it breakdown is called dielectric strength.
For example: Dielectric strength of air 3 X 106 V m-1
20. Define capacitance. Give its unit.
Answer Key:
The capacitance C of a capacitor is defined as the ratio of the magnitude of charge on either of the conductor plates to the potential difference existing between them.
C=QV
21. What is corona discharge ?
Answer Key:
1. The total charge of the charged conductor near the sharp edge reduces.
2. Leakage of charges from the sharp points to the charged conductor.
3. Corona discharge also known as "action of points"
III. Long answer questions.
1. Discuss the basic properties of electric charges.Answer Key:
1. Electric Charge :
- Objects in the universe are made up of atoms which made up of protons , neutrons, and electrons.
- These particles have mass , an inherent property of particles.
- Electric charge is another intrinsic and fundamental property of particles.
- The SI unit of charge is Coulomb.
2. Conservation of Charge :
- The total electric charge in the universe is constant. Charge can neither be created nor be destroyed.
- In any physical process net change in charge will always be zero.
- Objects are electrically neutral before rubbing process happen.
- After rubbing simply transfers charges from one object to the others.
Example :
1. When a glass rod rubbed with silk cloth then negative charge transferred from glass to silk.
2. As a result , glass rod is positively charged and silk cloth is negatively charged.
3. Quantisation of Charge:
- The
charge q on any object is equal to an integral multiple of fundamental unit of charge
e. This is called quantisation of electric charge. Charge of electron = - 1.6
X 10-19 C .
- q=ne
- n
is any integer (0 , + 1, +
2, + 3…)
- This
is called quantisation of charge.
2. Explain in detail Coulomb’s law and its various aspects.
Answer Key:1. Coulomb’s
law states that, Electrostatic force is directly proportional to the
product of the magnitude of the point charges and inversely
proportional to the square of the distance between two point
charges.
F→21=Fq1q2r2r^12
F21 = Force on point charge q2 exerted
by another point charge q1
q1 q2 = Point charges
r12 = Unit vector
2. The force on the charge q2 exerted by the charge q1 always lies along the line joining the two charges. r^12 is the unit vector pointing from charge q1 to q2 .
3. In SI units, and its value is 9 X 109 N m2 C-2. Here ε0 is the permittivity of free space or vacuum and its value is ∈∘=14πk=8.85×10-12C2N-1m-2
4. The magnitude of the electrostatic force between two charges each of one coulomb and separated by a distance of 1 m is calculated as follows: F=9×109×1×112=9×109N
5. In SI units, Coulomb’s law in vacuum
F→12=14π∈∘q1q2r2r^12
In a medium
F→12=14π∈q1q2r2r^12
6. Difference between Coulomb force and
gravitational force
|
S.No
|
Coulomb Force
|
Gravitational Force
|
|
1
|
It may be attractive or repulsive.
|
It is always attractive in nature.
|
|
2
|
It depends upon medium.
|
It does not depend upon the medium.
|
|
3
|
It is always greater in magnitude.
K=9x109 Nm2 C-2
|
It is lesser than coulomb force.
G=6.67x10-11 Nm2
Kg2.
|
7. The force on a charge q1 exerted by a point charge q2 is given by
F→12=14π∈∘q1q2r2r^21
Here r^12 is the unit vector from charge q1 to q2.
But r^21=-r^12
F→12=14π∈∘q1q2r2-r^12=-14π∈∘q1q2r2r^12
(or)F→12=-F→21
3. Define electric field and discuss its various aspects .
Answer Key:
Electric Field :
Electric field at a point P, at a distance r from the point charge q is the force experienced by a unit point charge.
Formula:
E→=F→q0=kqr2r^=14π∈0qr2r^
SI unit : N C-1
Important aspects of Electric field:
1. Force experienced by the test charge q0 is F→=q0E→
2. q is positive , electric field points away from the source .
3. q is negative , electric field points towards the source .
4. Electric field is independent of test charge q0 and depends only on source charge q.
5. Electric field is a vector quantity which has unique direction and magnitude .
6. As distance increases electric field decreases in magnitude.
7. Test charge q0 is small , not modify the electric field of source charge.
8. Electric field equation is only valid for point charges.
9. There are two kinds of the electric field. Uniform and non - uniform electric field.
10. Uniform electric field : Have same direction and constant magnitude at all points.
11. Non-uniform electric field : Different directions and different magnitudes or both at different points in space.
4. Calculate the electric field due to a dipole on its axial line and equatorial plane.
Answer Key:
Diagram:
Formula:
E→axial=14π∈02p→r3
Explanation:
Consider an electric dipole placed on the x-axis . A point C is located at a distance of r from the midpoint O of the dipole on the axial line. Electric dipole moment vector p→ is from -q to +q and is directed along BC.
i) Electric field due to a electric dipole on its axial line:
1. Electric field due to +q:
2. Electric field due to -q:
3. Total Electric field:
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
4. (r >> a) then (r2-a2)2 = r4
ii) Electric field due to a electric dipole on its Equatorial plane :
1. Let a point C at a distance r from the midpoint O of the dipole on equatorial plane .
2. The point C is equi distant from +q and – q , magnitude of the electric fields is same.
3. E→+ and E→- can be resolved into two components.
4. One component parallel to dipole axis and other perpendicular to it.
5. Perpendicular components |E→+| sinθ and |E→-| sinθ equal in magnitude oppositely directed , they cancel each other.
6. Magnitude of total electric field is sum of the parallel component of E→+,E→- direction along p^
Diagram:Formula:
E→tot=-14π∈0p→r3At very large distance (r>>a) then (r2 + a2)3/2
= r3
E→tot=-14π∈0p→r3
5. Derive an expression for the torque experienced by a dipole due to a uniform electric field.
Answer Key:
Diagram:
Torque on dipole due to uniform electric field:
1. Consider an electric dipole moment p→ placed in a uniform electric field E→.
2. Charge +q experience a force:qE→
3. Charge -q experience a force:-qE→
4. Total force acts on the dipole is zero. But two forces constitute a couple.
5.The dipole experience a torque tends to rotate the dipole.
Derivation:
1. τ→=OA→×(-qE→)+OB→×qE→
2. τ→=|OA→||(-qE→)|sinθ+|OB→||qE→|sinθ
3. τ→=qE.2asinθ
4. τ→=p→✕E→
Cases:
1.Magnitude of torque is τ=pE sin θ and is maximum when θ=90°.
2.If p→ is aligned with E→, the total torque on the dipole becomes zero.
6. Derive an expression for electrostatic potential due to a point charge.
Answer Key:
Diagram:%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
Formula:
V=14π∈0qr
Explanation:
Consider a positive charge q kept fixed at a origin . Let P be a point at distance r from charge q.
Derivation:
1. Electric potential at the point P:
V=∫∞r(-E→).dr→=-∫∞rE→.dr
2. Electric field due to positive point charge q:E→=14π∈0qr2r^
3. V=-14π∈0∫∞rqr2r.^dr→
4. The infinitesimal displacement vector dr→=drr^ and using r^.r^=1
5. V=-14π∈0∫∞rqr2r.^drr^=-14π∈0∫∞rqr2dr
6. V=-14π∈0q{-1r}r¥ =14π∈0qr
Cases:
|
Charge q
|
Potential
|
V Value
|
Distance
|
|
Positive
|
V=14π∈0qr
|
Decreases
|
Increases
|
|
Neagative
|
V=14π∈0qr
|
Increases
|
Increases
|
7. Derive an expression for electrostatic potential due to an electric dipole.
Answer Key:
Diagram:
Formula:
V=14π∈∘p→.r^r2
Explanation
Consider two equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance 2a.
The point P is located at a distance r from the midpoint of the dipole.
Let θ be the angle between the line OP and dipole axis AB.
Let r1 be the distance of point P from +q. Let r2 be the distance of point P from -q.
Derivation:
1. Potential at P due to charge +q: =14π∈∘qr1
2. Potential at P due to charge -q: =-14π∈∘qr2
3. Total Potential: V=14π∈∘q(1r1-1r2)
Special cases:
8. Obtain expression for potential energy due to collection of three point charges which are separated by finite distance.
Diagram:
Formula:
U=14π∈∘[q1q2r12+q1q3r13+q2q3r23]
Explanation :
1. Bringing a charge q1 from infinity to the point A requires no
work .
2. To bring the second
charge q2 to the point B , work must be done against the electric
field created by the charge q1
.
The work done on the charge q2
is W = 2V1B
. V1B is the electrostatic potential due to charge q1 at point B.
UI =14π∈∘q1q2r12
3. To bring the charge q3
to the point C, work must be done against
total electric field due to
both charges q1 and q2.
1. The work done to bring the charge
q3 is W = q3 ( V1C + V2C) 2. V1C is the
electrostatic potential due to charge q1 at point C.
3. V2C is the electrostatic potential due to charge
q2 at point C.
UII=14π∈∘[q1q3r13+q2q3r23]
4. Total electrostatic potential energy for the system of charges.
UIII=14π∈∘[q1q2r12+q1q3r13+q2q3r23]
5. Electrostatic potential
is independent of configuration of charges since force is conservative one.
9. Derive an expression for electrostatic potential energy of the dipole in a uniform electric field.
Diagram:
Formula:
U=-pEcosθ=-p→.E→
Explanation:
1. Consider a dipole
placed in the uniform electric field E→.
2. A dipole
experiences a torque when kept in an uniform electric field E→.
3. This torque
rotates the dipole to align it with the direction of the electric field.
4. Rotate the dipole
from its initial angle θ to another angle θ′against the torque.
5. An equal and
opposite external torque must be applied on the dipole.
Derivation:
1. Work done by the external torque W=∫θ'θτextdθ →(1)
2. |τ→ext|=|τ→E|=|p→xE→| → (2)
3. Substituting equation (2) in equation (1), we get
W=∫θ'θpEsinθdθ
4. This work done is equal to the potential
energy difference.
U(θ)-U(θ′)=∆U=-pEcosθ+pEcosθ′
5. Initial angle
is θ′= 90° as reference point , then U (θ′)=pEcos90°=0
6.
Potential energy: U(θ) = - pEcosθ = -p→.E→
Cases :
1. Potential energy
is maximum when dipole is aligned anti – parallel ( θ = π ) to
electric field.
2. Potential energy
is minimum when dipole is aligned parallel ( θ = 0 ) to the external electric field.
10. Obtain Gauss law from
Coulomb’s law.
Gauss’s law states that if a charge Q is enclosed by an arbitrary closed surface, then the total electric flux ΦE through the closed surface is ΦE∮E→.dA→=Qencl∈∘ Diagram:
Formula:
ΦE∮E→.dA→=Qencl∈∘
Derivation:
1. A positive point charge Q is surrounded by an imaginary sphere of radius r.
2.The total electric flux through the closed surface of the sphere using
ΦE∮E→.dA→=∮EdA cosθ
3. dA→ is along the electric field E→ and �θ=0°. ΦE=∮EdA Since cos0°=1
4. E is uniform on the surface of the sphere, ΦE=E∮dA.
5. Substituting for � ∮dA= 4πr2 and E=14π∈0Qr2 in equation, we get
ΦE=14π∈∘Qr2×4πr2=4π14π∈∘
ΦE=Q∈∘
6. The equation is called as Gauss’s law.
11. Obtain the expression for electric
field due to an infinitely long charged wire.
Diagram:
Formula:
E→=12π∈∘λrr^
Theory
:
1. Consider an infinitely long
straight wire having uniform linear charge density λ .
2. Let P be a point located at a
perpendicular distance r from the wire. The electric field can be found using Gauss law.
3. Two small charge elements A1
,A2 on the wire which are at equal distances from
point P.
4. Resultant electric field due to two
charge elements points radially away from charged wire.
5. The magnitude of electric field is
same at all points on the circle of radius r.
6. The charged wire possesses a
cylindrical symmetry, Gaussian surface
of radius r and length L.
Derivation:
1. Total
electric flux through the closed surface ΦE=∮E.→dA→
2. ∫ Curved surface E.→dA→+∫ top surfaceE.→dA→+∫ bottom surfaceE.→dA→
3. For the curved surface: E is
parallel to A
then , E . d
A =
E d A
4. For the top and bottom surface
: E
is perpendicular to A then ,
E . d A
= 0 .
5. Applying Gauss law to the cylindrical surface , ΦE=∫ Curved surfaceEdA=Qenclϵο
6. The magnitude
of the electric
field for the
entire curved surface
is constant. 7. Linear charge
density (charge per unit length) : ΦE=∮E.→dA→∫ Curved surfaceE.→dA→+∫ top surfaceE.→dA→+∫ bottom surfaceE.→dA→ΦE=∫ Curved surfaceEdA=QenclϵοE ∫ Curved surfacedA=λLϵο∫ Curved surfacedA=2πrLE.2πrL =λLϵοE=12πϵολrE→=12πϵο λr r^Qencl=λL8. E ∫ Curved surfaced A=λLϵο
9. Total area of the curved surface : ∫ Curved surfaced A=2πrL
10. E.2πrL =λLϵο
11. Electric field due to infinite long charged
wire: E=12πϵολr
12. In vector form: E→=12πϵο λr r^
13. If λ >
0 then E
points perpendicularly
outward ( r
) from the wire.
14. If λ < 0 then
E points perpendicularly inward
( - r ) from the wire
12. Obtain the expression for electric field due to a charged infinite plane
sheet.
Diagram:
Formula:
E→=σ2 ϵοn^
Explanation:
1.An
infinite plane sheet of charges with uniform surface charge density σ
2. Let
P be a point at a distance r from the sheet.
3.
The electric field should be same at all
points equidistant from the plane.
4. A
cylindrical Gaussian surface of length 2r and two flats surface each of area A
is chosen.
5. The
infinite plane sheet passes perpendicularly through the middle part of the
Gaussian surface.
Derivation:
1. Total electric flux linked with the
cylindrical surface ΦE=∮E→.dA→
2. ΦE==∫Curved surfaceE→.dA→+∫PE→.dA→+∫P'E→.dA→=Qenclϵο
3. For
curved surface : Electric field is
perpendicular to the area ΦE==∫Curved surfaceE→.dA→+∫PE→.dA→+∫P'E→.dA→=Qenclϵο
4. At
P and P : Electric
field is parallel to the area element
at all points. 5. By
applying Gauss law , ΦE=∫PEdA+∫P'EdA=Qenclϵο
6. Magnitude of the
electric field at these
two equal flat
surfaces is uniform , E is taken out of the integration .
7. Qencl=σA
8. 2E ∫PdA=σAϵο
9. The
total area of
surface either at
P and ∫PdA=A
10. 2EA=σAϵο
11. E→=σ2 ϵο
12. In
vector form E→=σ2 ϵοn^
13.
If σ
> 0 then
E points perpendicularly outward
to the plane (n).
14. If σ < 0 then
E points perpendicularly inward to the plane (-n).
13. Obtain the expression for electric field due to a uniformly charged
spherical shell.
1. Consider a uniformly charged
spherical shell of radius R and total
charge Q
.
2. The electric field at points outside and inside the sphere can be
found using Gauss law.
Case i : At a point outside the shell (
r > R )
For point outside the spherical shell , a large spherical Gaussian
surface is drawn .
1. Let us choose a point P outside
the shell at a distance r from the
centre.
2. The charge is uniformly distributed on the surface of the sphere. (
spherically symmetry )
3. The electric field must point radially outward if Q
> 0. 4. The electric field must point radially
inward if Q <
0.
Derivation:
1. Applying Gauss law: ∮Gaussian surfaceE→.dA→
2. E ∮Gaussian surfacedA=Qϵο
3. ∮dA = total
area of Gaussian
surface = 4π r2
Gaussian Surface
4. E.4 π r2 = Qϵο
5. E=14πϵοQr2
6. In
vector form, E→=14πϵοQr2r^ |
7. The electric field must point radially outward if Q
> 0 and
radially inward if Q <
0.
Case ii : At a point on the surface of
the spherical shell (r = R)
E→=14πϵοQR2r^ The electric field at points on the
spherical shell (r =
R) is given by
|
Case iii : At a
point inside the spherical shell (r < R)
For point outside the spherical shell , a spherical Gaussian surface
smaller than the spherical shell 1. Consider a point P inside the shell at a distance r from the
centre. A Gaussian sphere of radius r is constructed .
2. Applying Gauss law: ∮Gaussian surface E→.dA→=Qϵο
3. E.4πr2=Qϵο
4. Gaussian surface encloses no
charge,
Q = 0
then E =
0 (r < R)
5.
Electric field due to the uniformly charged spherical shell is zero at all
points inside the shell.
14. Discuss the
various properties of conductors in electrostatic equilibrium.




%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)


%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)



%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)



%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)

%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)


%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)
%20-%20English%20Medium%20Guides.PNG)









0 Comments:
Post a Comment